The impact of socio-cultural learning tasks on students’ foreign grammatical language awareness
A study conducted in German post-DESI EFL classrooms
Summary
Excerpt
Table Of Contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- About the author(s)/editor(s)
- About the book
- This eBook can be cited
- Table of Contents
- Introductory remarks
- List of Tables and Figures
- Preface
- 1. Introduction
- 1.1 Incentive for this dissertation
- 1.2 The DESI study
- 1.3 DESI and its conceptualization of “language awareness”
- 1.4 DESI and “language awareness” – results
- 2. Aims and objectives
- 2.1 DESI within the scope of this dissertation
- 2.1.1 Sample groups
- 2.1.2 DESI and its results – teachers’ perspectives
- 2.1.3 DESI and its results – learners’ perspectives
- 2.1.4 Précis
- 2.2 The DESI test in forms 9b and 9c
- 2.2.1 Test format and implementation
- 2.2.1.1 Test results
- 2.2.1.1.1 Test results 9b
- 2.2.1.1.2 Test results 9c
- 2.2.1.2 Comparison and evaluation of test results
- 2.2.2 “Grammatical language awareness” – narrowing down the matter
- 2.2.3 Practical aim
- 2.3 DESI and its explanatory assumptions
- 2.3.1 The role of self- and peer- correction
- 2.3.1.1 The role of autonomous language production, self- and peer- correction – teachers’ perspectives
- 2.3.1.2 Précis
- 2.4 Perspectives on teaching, learning, and the language learner
- 2.4.1 Investigating teachers’ perspectives
- 2.4.1.1 The language learner
- 2.4.1.2 Learning a foreign language
- 2.4.1.3 Teaching a foreign language
- 2.4.1.4 Précis
- 2.4.2 The researcher’s perspective
- 2.4.3 Teachers’ perspectives and classroom realities
- 2.4.4 Investigating students’ perspectives
- 2.4.4.1 Affective factors and motivation
- 2.4.4.2 Teaching and learning
- 2.4.4.3 Précis
- 2.4.5 Alternative explanatory assumption
- 2.5 Theoretical aim
- 2.6 Research question and hypothesis
- 3. Theoretical framework
- 3.1 PPP – a traditional teaching and learning method
- 3.1.1 Definition and theoretical rationale
- 3.1.2 Précis
- 3.1.3 Implications of PPP
- 3.2 Task-based language teaching and learning (TBLT/L)
- 3.2.1 Task definition
- 3.2.2 Task definition – the researcher’s perspective
- 3.2.3 Theoretical rationale
- 3.2.4 Task-supported language teaching and learning (TSLT/L)
- 3.2.5 Précis
- 3.2.6 Implications of TBLT/L and TSLT/L
- 3.3 “Tasks” and the teaching of grammar
- 3.3.1 General concepts
- 3.3.2 Specific task types
- 3.3.3 Précis
- 3.3.4 Implications of the intersection of “grammar” and “tasks”
- 3.4 Where TBLT/L meets socio-cultural theory
- 3.4.1 Language and language learning
- 3.4.2 Task research and socio-cultural theory
- 3.4.3 Précis
- 3.5 Where socio-cultural theory meets TBLT/L
- 3.5.1 Language learning
- 3.5.2 Socio-cultural theory and task research
- 3.5.3 Précis
- 3.6 The interplay of TBLT/L and socio-cultural theory – unmet challenges
- 3.6.1 Different research foci
- 3.6.2 Attempts to combine different research foci
- 3.6.3 Implications of “unmet challenges”
- 3.7 Major tenets of socio-cultural theory
- 3.7.1 Establishing the basis of socio-cultural theory – L. S. Vygotsky
- 3.7.2 Précis
- 3.7.3 Extensions of Vygotsky’s work – P. J. Galperin
- 3.7.3.1 On “internalization”
- 3.7.3.2 The “stage-by-stage formation of mental actions”
- 3.7.3.3 On the use of “schemes”
- 3.7.3.4 Précis, critical reflection and implications
- 3.7.3.5 Pedagogic implications
- 3.7.4 A.N., A.A. and D.A. Leontiev
- 3.7.5 Refining the use of “external aids” – A.R. Luria
- 3.7.6 “Thinking in a foreign language” – B.V. Belyayev
- 3.7.7 Implications of socio-cultural theory
- 3.8 Constructs to be measured
- 3.8.1 Reported Speech
- 3.8.1.1 Reported Speech in the official teaching curriculum
- 3.8.1.2 Reported Speech in authentic and pedagogic grammars
- 3.8.1.3 Reported Speech in the main study tests
- 3.8.2 Implicit and explicit knowledge
- 3.8.2.1 Implicit and explicit Reported Speech knowledge
- 3.8.3 Measurement of implicit and explicit knowledge
- 3.8.3.1 Measurement of implicit and explicit Reported Speech knowledge
- 3.8.4 Ways of expressing the past
- 3.8.4.1 Past Tenses in the official teaching curriculum
- 3.8.4.2 Past Tenses in authentic and pedagogic grammars
- 3.8.4.3 Past Tenses in the main study tests
- 3.8.5 Implicit and explicit Past Tenses knowledge
- 3.8.6 Measurement of implicit and explicit knowledge
- 3.8.6.1 Measurement of implicit and explicit Past Tenses knowledge
- 4. Development of stimulus material for the main study
- 4.1 Major insights from the pilot study
- 4.2 Reported Speech “socio-cultural learning tasks”
- 4.2.1 “Task” components
- 4.2.2 “Socio-cultural” components
- 4.3 Past Tenses “socio-cultural learning tasks”
- 4.3.1 “Task” components
- 4.3.2 “Socio-cultural” components
- 4.4 Emphases of “task-” and “socio-cultural” components
- 4.5 Reported Speech PPP
- 4.6 Past Tenses PPP
- 4.7 Development of pre-, post-, and delayed post-tests
- 4.7.1 Test trials
- 4.7.2 Item analyses
- 4.8 Ways of measurement reconsidered – a critical reflection
- 5. PPP and SCLTs put to the test – the main study
- 5.1 Objectives
- 5.2 Overall design
- 5.3 Sampling procedures
- 5.3.1 Sample groups
- 5.3.1.1 The treatment group
- 5.3.1.2 The control group
- 5.3.1.3 The role as a teacher-researcher
- 5.4 Implementation of stimulus material
- 5.4.1 Past Tenses in the treatment group
- 5.4.1.1 Lesson one
- 5.4.1.2 Lesson two
- 5.4.1.3 Lesson three
- 5.4.1.4 Lesson four
- 5.4.2 Past Tenses in the control group
- 5.4.2.1 Lesson one
- 5.4.2.2 Lesson two
- 5.4.2.3 Lesson three
- 5.4.2.4 Lesson four
- 5.4.3 Reported Speech in the treatment group
- 5.4.3.1 Lesson one
- 5.4.3.2 Lesson two
- 5.4.3.3 Lesson three
- 5.4.3.4 Lesson four
- 5.4.4 Reported Speech in the control group
- 5.4.4.1 Lesson one
- 5.4.4.2 Lesson two
- 5.4.4.3 Lesson three
- 5.4.4.4 Lesson four
- 5.5 Scoring systems
- 5.5.1 Scoring system Reported Speech
- 5.5.1.1 Implicit knowledge
- 5.5.1.2 Explicit knowledge
- 5.5.2 Scoring system Past Tenses
- 5.5.2.1 Implicit knowledge
- 5.5.2.2 Explicit knowledge
- 5.6 Statistic analyses – general remarks
- 5.7 Statistic analyses – results
- 5.7.1 Reported Speech implicit knowledge
- 5.7.2 Reported Speech explicit knowledge
- 5.7.3 Précis
- 5.7.4 Past Tenses implicit knowledge
- 5.7.5 Past Tenses explicit knowledge
- 5.7.6 Précis
- 5.8 Statistic results revisited
- 5.8.1 Research questions and hypotheses revisited
- 5.8.2 Causal explanations
- 5.8.3 Alternative causal explanations
- 6. Theoretical and practical implications
- 6.1 Theoretical and practical aims reconsidered
- 6.2 External validity and replication
- 6.2.1 External validity defined
- 6.2.2 Threats to external validity
- 6.2.3 Ways to approach external validity
- 6.3 Implications, research ethics and further research desiderata
- 6.4 Concluding remarks
- Appendix
- Chapter 2
- Teacher questionnaire
- Student questionnaire
- Chapter 3
- Relation of implicit and explicit scores
- Treatment group Past Tenses
- Control group Past Tenses
- Chapter 4
- Treatment group Reported Speech worksheet 1 (=control group text 1)
- Treatment group Reported Speech worksheet 2 (=control group text 2)
- Treatment group Reported Speech worksheet 3 (=control group text 3)
- Treatment group Reported Speech worksheet 4 (=control group text 4)
- Treatment group Reported Speech “external aids”
- Control group Past Tenses worksheet 1
- Control group Past Tenses worksheet 2
- Control group Past Tenses worksheet 3
- Control group Past Tenses worksheet 4
- Control group Past Tenses transparency
- Results of item analyses
- Final test version Past Tenses
- Final test version Reported Speech
- Final Reported Speech test
- Final Past Tenses test
- Chapter 5
- Validation questionnaire
- Treatment group Past Tenses worksheets 2
- Treatment group Past Tenses worksheets 3
- Treatment group Past Tenses transparency
- Treatment group Past tenses worksheets 4
- Treatment group Reported Speech transparency
- Index of acronyms
- References
- Further readings
| 13 →
The need to learn foreign languages is omnipresent in most present-day societies. Multilingualism paves today’s students the way to act as successful and responsible participants in societies tomorrow. It enables them to meet challenges posed by globalisation and continuous changes in the world of work. It allows them to live in and shape peaceful multicultural societies. In this context, the English language has a somewhat exceptional position: For those people who do not grow up with it as a mother tongue, it has become lingua franca, a tool to ensure communication throughout the entire world. This being the case, research which aims at illuminating the interplay of teaching and learning English as a foreign language cannot be valued highly enough. The same is true for the development of teaching and learning methods which help teachers cope with growing demands of heterogeneous classrooms, and students to master foreign languages in an efficient and durable manner. The dissertation at hand is nested precisely in this framework. For the author, the desire to contribute to the theoretical – and practical – development of promising ways of teaching and learning was the driving force to conduct the studies presented.
At this point, let me express my gratitude to the people who accompanied my work. I am indebted to Prof. Dr. Ehrhart for her decision to supervise my dissertation, and for her excellent (and on-going) support. She always gave me the feeling that my research matters. I would like to thank Prof. Dr. Krolak-Schwerdt for introducing me to the world of statistics, and for challenging and enriching my ideas. I was extremely lucky to be one of Prof. Dr. Kühlwein’s students years ago. He ignited my passion for linguistics and continuously supported my research. Dr. Pit-ten Cate, Dr. Böhmer and Prof. Dr. Artelt spent much of their precious time on the realisation of my project. Thank you so much. Further, I am grateful to my school principals, OStD Klenner and OStD Fries, to my colleagues, students and their parents whose understanding and flexibility paved the way to data collection in authentic pedagogical situations. I wholeheartedly wish to thank my parents, whose inexhaustible love and support throughout the past decades have been an indispensable source of vigour.
| 15 →
Table
| 1 | Chronology of the Pilot Study |
| 2 | Chronology of Test Triallings and the Main Study |
| 3 | DESI “Grammatical Language Awareness” Competence Levels |
| 4 | DESI “Grammatical Language Awareness” Test Item: Example (1) |
| 5 | DESI “Grammatical Language Awareness” Test Item: Example (2) |
| 6 | DESI “Grammatical Language Awareness” Test Results/Mistake Ranking (9b/9c) |
| 7 | DESI “Grammatical Language Awareness Test”: Distribution of Mistakes (9b) |
| 8 | DESI “Grammatical Language Awareness Test”: Distribution of Mistakes (9c) |
| 9 | Validation Results Reported Speech for Treatment Group (TG) and Control Group (CG) |
| 10 | Validation Results Past Tenses for Treatment Group (TG) and Control Group (CG) |
| 11 | Descriptive Statistics for Reported Speech Implicit Knowledge by Group |
| 12 | Descriptive Statistics for Mann Whitney U Test |
| 13 | Descriptive Statistics for Reported Speech Explicit Knowledge by Group |
| 14 | Descriptive Statistics for Mann Whitney U Test |
| 15 | Descriptive Statistics for Past Tenses Implicit Knowledge by Group |
| 16 | Descriptive Statistics for Mann Whitney U Test |
| 17 | Descriptive Statistics for Past Tenses Explicit Knowledge by Group |
| 18 | Descriptive Statistics for Mann Whitney U Test |
| 19 | Treatment Group Evaluation of Reported Speech and Past Tenses Training units |
| 20 | Control Group Evaluation of Reported Speech and Past Tenses Training Units ← 15 | 16 → |
Figure
| 17 →
The chapters to follow provide insights into ways of fostering German 9th grade EFL students’ “grammatical language awareness competencies” via “socio-cultural learning tasks” (SCLTs) which have been developed genuinely and solely for this purpose (pilot study). Thus, they primarily address SLA researchers from various strands, language test developers as well as in-service and trainee EFL teachers and students of linguistics and didactics.
The capacities SCLTs have to propel students’ competencies in the fields of “Past Tenses” and “Reported Speech” are compared with the traditional “presentation-practice-produce” (PPP) teaching approach (main study). Six major research steps are pursued: In chapter one, the catalyst for the dissertation is presented, namely the results of the official DESI study which uncovered 9th grade EFL students’ deficits in the field of “grammatical language awareness”. The overall practical aim to develop effective teaching means to propel students’ competencies in this field is specified in chapter two, which is devoted to the application of DESI results as a springboard for further research: These results are confirmed by teachers and students who participated in a pilot study which also served to identify “Reported Speech” and “Tenses” to be among the most challenging grammatical features for students. Readers are also offered a comprehensive account of possible root causes of students’ deficiencies, among which a neglect of “task-based” and “socio-cultural” elements in present-day EFL classrooms has been found to be the predominant one. Given this, the theoretical aim to develop “socio-cultural learning tasks” (SCLTs) by unifying aspects taken from “task-based-language teaching” and “socio-cultural learning theory” is evolved. Further, the question is raised as to what extent the implementation of SCLTs in EFL classrooms can stand comparison with or even outperform the traditional “presentation-practice-produce” (PPP) teaching approach in terms of students’ “grammatical language awareness development”.
Chapter three provides the theoretical background of the PPP approach and the design of SCLTs. A thorough examination of the intersections between “tasks” and the teaching of “grammar”, as well as between “Task-Based Language Teaching/Learning” (TBLT/L) and “socio-cultural learning theory” is offered, including a survey of the development of relevant socio-cultural tenets throughout the past decades. Based on these theoretical grounds and on unmet research challenges they breed, the researcher’s own definition of what constitutes SCLTs is gradually evolved. ← 17 | 18 →
Towards the end of the third chapter, the target features “Reported Speech” and “Past Tenses” which constitute the grammatical language awareness competencies of the students who participated in the main study are elaborated: The nature of explicit and implicit knowledge of both target features is presented, resulting in a portrayal of the main study pre-, post-, and delayed post-tests designed to measure students’ learning achievements.
Chapter 4 serves as a link between chapters 3 and 5 since it draws on the former when offering an account of Reported Speech and Past Tenses SCLTs, and on the latter when providing a detailed description of the planned training lessons which constitute the training units for the control and the treatment group (taught via PPP and SCLTs, respectively) in the main study. Internal validity issues of the quasi-experimental main study are addressed in chapter 5, within which the ways the training lessons developed in the previous chapter actually evolved in the control and treatment group training units are presented. In the further course of this chapter, readers are informed about the scoring systems applied to the pre-, post- and delayed post-tests which framed the main study, as well as the statistical analyses conducted to uncover the effects the independent variables (PPP and SCLTs) had on the dependent ones (students’ grammatical language awareness development). In the last sections of the fifth chapter, research questions and hypotheses are reconsidered and statistical results critically reinvestigated.
Chapter 6 incorporates theoretical and practical implications of the main study, issues of external validity as well as the need and suggestions for further research.
To ease the reading process,1 chronologies of studies conducted and data collection tools employed are provided in Tables 1 and 2.2 Note that six different 9th grade forms/classes are mentioned in the chronologies: Two (9b/9c) took part in the pilot study (2009/2010), two (9b/9c)3 underwent the test trialling phase (2012), and two (9a/9c) participated in the main study (2012). Most parts of the pilot study, apart from the teacher and student questionnaires (cf. chapter 2) are only briefly recapitulated (predominantly in chapter 4, section 4.1). For the interested reader, a detailed account of the pilot study is available on demand. ← 18 | 19 →
Table 1: Chronology of the Pilot Study
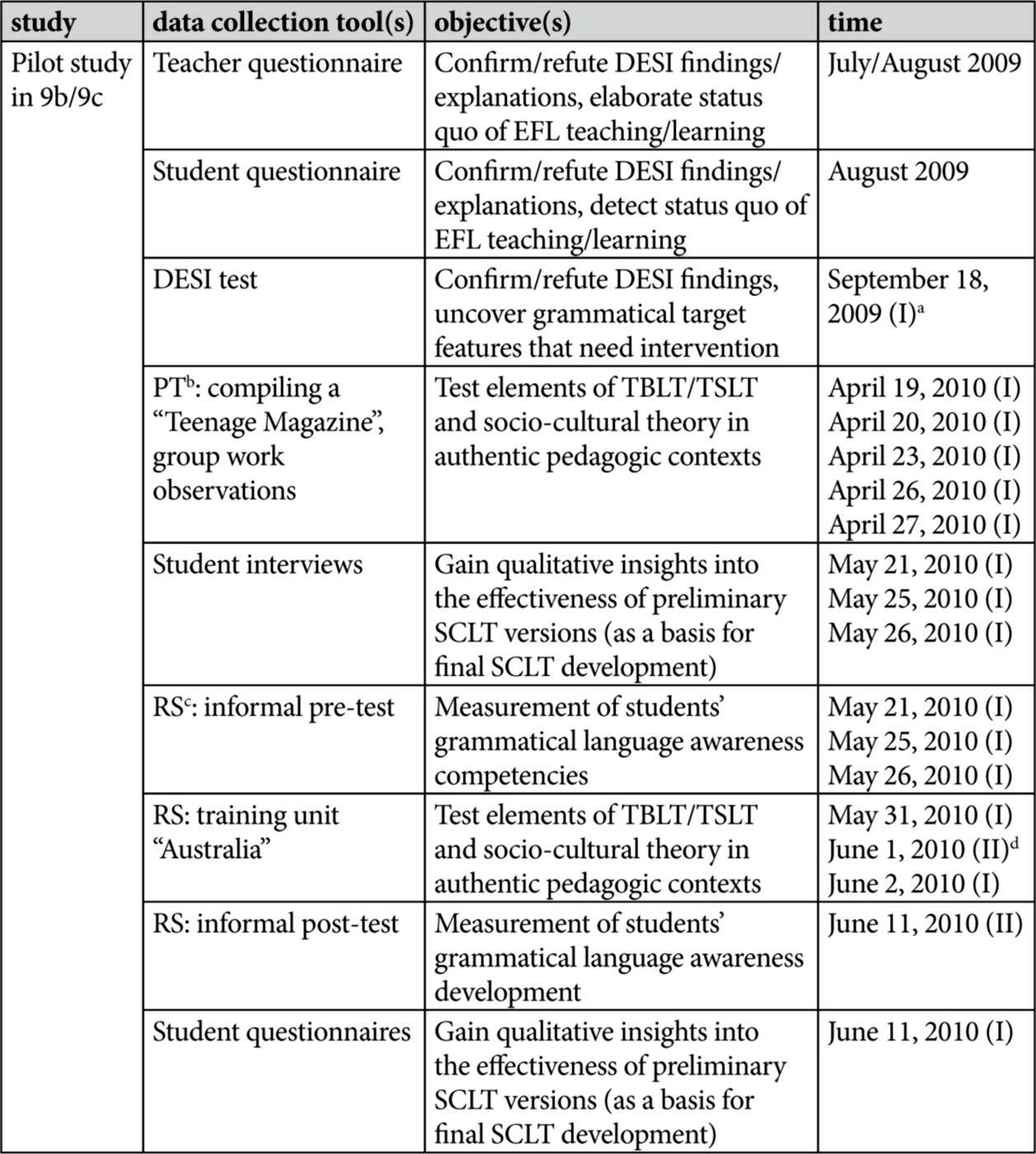
aOne lesson (45 min.). bPast Tenses. cReported Speech. dTwo lessons (90 min.). ← 19 | 20 →
Table 2: Chronology of Test Triallings and the Main Study
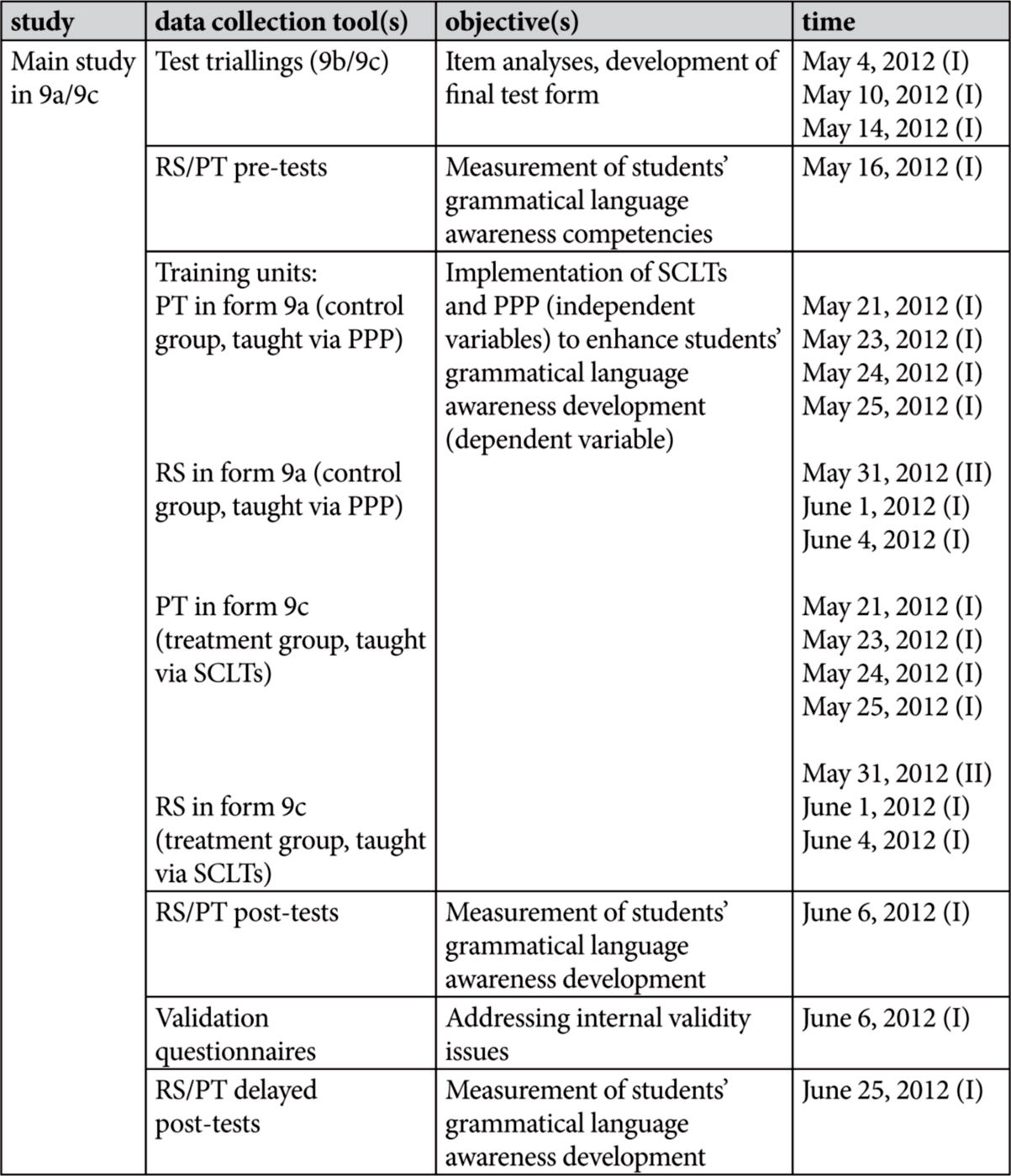
Since the studies necessitated the collection, analyses, publication and storage of sensible data, the approval of bodies involved including the school, parents, students and the data protection commissioner of Rhineland-Palatinate had been obtained in advance. Participation in the pilot study was voluntarily, that is students could drop out any time without giving any reasons. This, however, did not happen. As for the main study, students’ data were anonymized for analyses.
1 Note: The expressions “the researcher” and “the teacher-researcher” refer to the author of this dissertation.
2 Tenses in each chapter owe to these chronologies.
Details
- Pages
- 294
- Publication Year
- 2015
- ISBN (Hardcover)
- 9783631665763
- ISBN (PDF)
- 9783653060102
- ISBN (MOBI)
- 9783653949582
- ISBN (ePUB)
- 9783653949599
- DOI
- 10.3726/978-3-653-06010-2
- Language
- English
- Publication date
- 2015 (July)
- Keywords
- grammar internalization zone of proximal development ZPD quasi-experimental study
- Published
- Frankfurt am Main, Berlin, Bern, Bruxelles, New York, Oxford, Wien, 2015. 294 pp., 20 tables, 16 graphs
- Product Safety
- Peter Lang Group AG

